How To Read A Tukey Post Hoc Test
One common and popular method of post-hoc analysis is Tukeys Test. However you should only run one post hoc test do not run multiple post hoc tests.
Https Rpubs Com Aaronsc32 Post Hoc Analysis Tukey
Plantlm.

How to read a tukey post hoc test. ANOVA in this example is done using the aov function. The post hoc test well run is Tukeys HSD Honestly Significant Difference denoted as Tukey. P adj is the p-value adjusted for multiple comparisons using the R function TukeyHSDFor more information on why and how the p-value should be adjusted in those cases see here and here.
It allows to find means of a factor that are significantly different from each other comparing all possible pairs of means with a t-test like method. Since Tukeys test is a post-hoc test we must first fit a linear regression model and perform ANOVA on the data. The first table presents the results of the group by group comparisons and are interpreted the same as the LSD tables.
The Bonferroni is probably the most commonly used post hoc test because it is highly flexible very simple to compute and can be used with any type of statistical test eg correlationsnot just post hoc tests with ANOVA. A post hoc Tukey test showed that the future alone and future belonging groups differed significantly at p 05. Click on Post Hoc at the bottom of the dialog box that appears with the output from your ANOVA.
Ill show them both below. This video demonstrates how to conduct an ANOVA with a Tukeys HSD post hoc test in SPSS. The test is known by several different names.
Well explain how it works when well discuss the output. The Tukey test is a post hoc test in that the comparisons between variables are made after the data has already been collected. There are two ways to present post hoc test resultsadjusted p-values and simultaneous confidence intervals.
The Tukey post hoc test is generally the preferred test for conducting post hoc tests on a one-way ANOVA but there are many others. When we are conducting an analysis of variance the null hypothesis considered is that there is no difference in treatments mean so once rejected the null hypothesis the question is what. Click on Post Hoc select Tukey and press Continue Click on Options select Homogeneity of variance test and press Continue Press the OK button and your result will pop up in the Output viewer.
The results of pairwise comparisons with a Bonferroni correction ar. It is a post-hoc analysis what means that it is used in conjunction with an ANOVA. The Tukey test is popular so we will focus on that one.
The output for the Tukey post hoc test combines the output formats of the LSD and S-N-K post hoc tests. Tukeys test compares the means of all treatments to the mean of every other treatment and is considered the best available method in cases when confidence intervals are desired or if sample sizes are unequal Wikipedia. Homogeneity tests includes Levenes test for equal variances in our output.
This differs from an a priori test in which these comparisons are made in advance. Its not my intent to study in depth the ANOVA but to show how to apply the procedure in R and apply a post-hoc test called Tukeys test. There are a variety of post hoc tests you can choose from but Tukeys method is the most common for comparing all possible group pairings.
Yes you can interpret this like any other p-value meaning that none of your comparisons are statistically significant. We can see from the table below that there is a statistically significant difference in time to complete the problem between the group that took the beginner course and the intermediate course p 0046 as. If you find a significant result with a 1-Way Between Subjects ANOVA and if your IV has 3 levels you will need to use the results of a post hoc test like the Tukey test to compare ü Condition 1 and Condition 2 ü Condition 1 and Condition 3.
In the former case you might look at the mile run times of students in three different phys-ed classes one year. Select more than one test if you want to compare results. If your data met the assumption of homogeneity of variances use Tukeys honestly significant difference HSD post hoc test.
Estimates of effect size refers to partial eta squared. For a one-way ANOVA you will probably find that just two tests need to be considered. Post hoc comparisons using the Tukey HSD test indicated that the mean score for the sugar condition M 420 SD 130 was significantly different than the no sugar condition M 220 SD 084.
Step 2 Click on one of the Post Hoc tests listed under Equal Variances Assumed such as Tukey Duncan or Scheffe if you assume there are equal variances. The traditional Bonferroni however tends to lack power Olejnik Li Supattathum Huberty 1997. The misfortune control group was not significantly different from the other two groups lying somewhere in the middle.
However the a little sugar condition M 360 SD 089 did not significantly differ from the sugar and no sugar conditions 4. The Tukey test Tukey test is a single-step multiple comparison procedure and statistical test.
 One Way Anova And Post Hoc Test Using Spss Youtube
One Way Anova And Post Hoc Test Using Spss Youtube
 Using Post Hoc Tests With Anova Statistics By Jim
Using Post Hoc Tests With Anova Statistics By Jim
How Do I Report A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova In Apa Style
 Post Hoc Tests Tukey Honestly Significant Difference Test Sage Research Methods
Post Hoc Tests Tukey Honestly Significant Difference Test Sage Research Methods

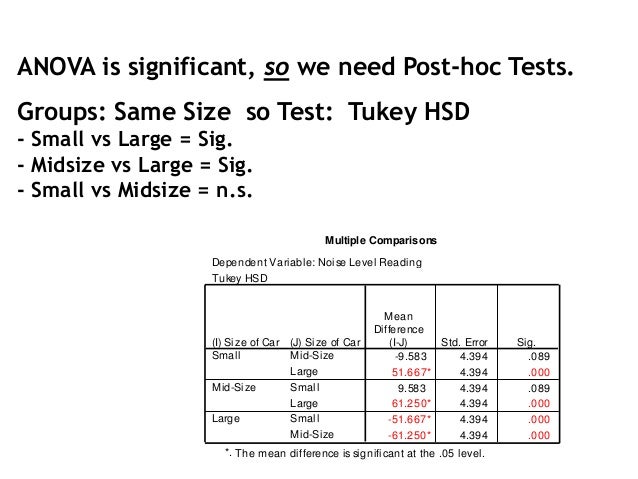 Two Way Anova Overview Spss Interpretation
Two Way Anova Overview Spss Interpretation
 How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology
How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology
 Research Methodology Digitalis Tankonyvtar
Research Methodology Digitalis Tankonyvtar
 Spss One Way Anova With Post Hoc Tests Simple Tutorial
Spss One Way Anova With Post Hoc Tests Simple Tutorial
 How To Obtain The Results Of A Tukey Hsd Post Hoc Test In A Table Showing Grouped Pairs Cross Validated
How To Obtain The Results Of A Tukey Hsd Post Hoc Test In A Table Showing Grouped Pairs Cross Validated
 12 7 Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Post Hoc Test Youtube
12 7 Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Post Hoc Test Youtube
How Do I Interpret Data In Spss For A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova
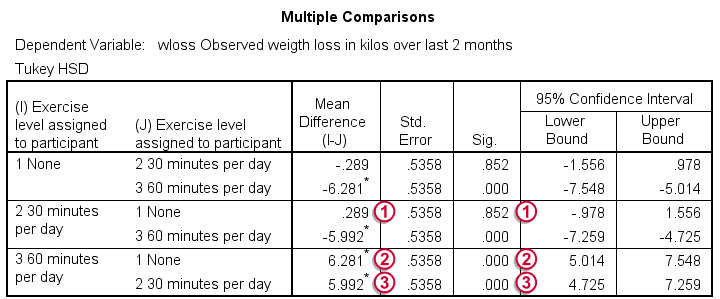 Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial
Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial
 J6 Two Way Anova Post Hoc Tests Youtube
J6 Two Way Anova Post Hoc Tests Youtube
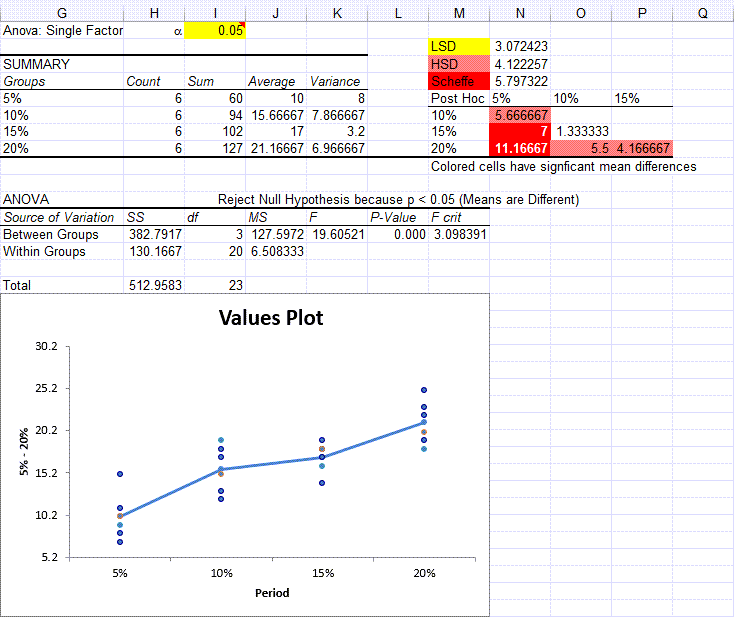 One Way Anova Post Hoc Tests In Excel
One Way Anova Post Hoc Tests In Excel
 Meaning Of Post Hoc Multiple Comparisons Cross Validated
Meaning Of Post Hoc Multiple Comparisons Cross Validated

